As our world becomes more technologically centered, it also becomes more data-centered. The modern world ebbs and flows with the transfer, collection, and exchange of data. It’s estimated that by 2025, 463 exabytes of data will be created each and every day. For clarity, one exabyte is equivalent to 1 billion gigabytes, or 1 million terabytes.
That data problem isn’t just something the tech industry is facing. With nearly every facet of modern business being digitized today, every sector is dealing with more data than they know what to do with. Honing in on just the automotive sector, the space is rapidly evolving its manufacturing capabilities and production possibilities through the leveraging of their data, in particular, through blockchain.
While blockchain may be familiar to most thanks to its recent application in cryptocurrencies, the theories and underlying science of the technology have been around since the early 1980s.
Blockchain is being explored by automotive manufacturers as a process that could be used to increase vehicle security, improve manufacturing, and even manage parts and suppliers in a more efficient manner.
As cars get more connected, more customizable, and more complex, the data problem in the automotive industry becomes more and more complex, and less easy to track. This problem is one example of the way that blockchain can be implemented to increase productivity.
To many, blockchain is just a complicated way to deal with data, and not something that concerns most people. But in actuality, this technology is a breakthrough in process. So, how does it work in reference to the automotive industry, and why is it so fundamentally different from its predecessors?
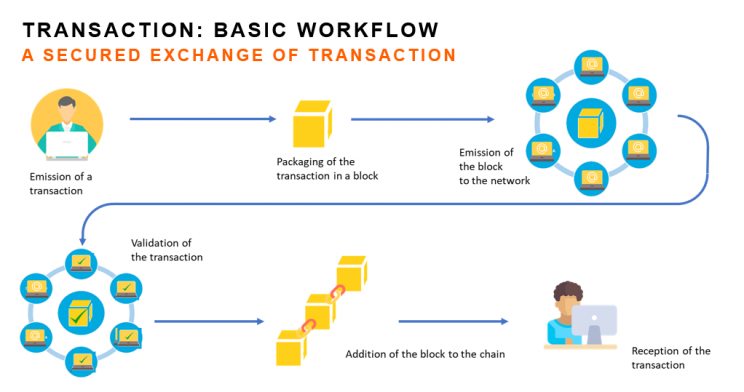
As a quick refresher, a blockchain is essentially a distributed secure database. Every transaction is represented as a digital “block”. This block is broadcast to every computer in the network, which must then verify that the transaction is valid. Once this has been done, the block is added to the chain of transactions. This chain is a permanent record of all of the transactions in the network.
Once they have been added to the chain, the blocks of data cannot be changed, copied or deleted, which makes blockchain very secure. Each block has a timestamp and a connection to a previous block. This results in the inability to change blocks, or stored data, without also influencing the other blocks around it.
The only way that a block can be edited is through the blockchain, and through encryption that each user owns, securely tracking all the changes through the connected blocks.
In reference to the automotive industry though, think of it like this:
An original equipment manufacturer (OEM) may work with hundreds of different suppliers to build one car. All the data for these parts has to be managed somehow, and if one part from one supplier is off in tolerance, or arrives late, the entire workflow can be held up. What the blockchain allows is for all of this data to be collected, securely, into one distributed system. Each supplier would have their own key to access their portion of the blockchain, which would be connected and combined with all of the other suppliers.
RELATED: WHAT IS THE FUTURE OF BLOCKCHAIN AND ADVERTISING
The result is that the OEM, and the suppliers themselves, have a fully secured and fully trackable file management system. All through the power of blockchain.
It’s the security and tracking aspects of blockchain tech that make it so versatile. Because all of the data is linked together and only changeable through secure cryptography, it’s the perfect system for storing medical records, financial transactions, and of course, automotive data.
Automotive manufacturing is a sector that demands constant innovation. Because OEMs have to deal with the ever-changing 21st-century manufacturing process, it’s no wonder that blockchain has been adopted as one of the innovations for the future.
Automotive manufacturers also have to deal with something that many manufacturers don’t – a huge amount of regulations (in more than a hundred domains, such as safety and emissions) that vary by region and geography. There is a wide range of issues surrounding ensuring compliance in automotive safety. And this is another problem that can be solved with the blockchain.
One of the best examples of using this tech to solve issues of compliance comes from the automotive manufacturer Groupe Renault. They developed a system called the Extended Compliance End-to-End Distributed, or XCEED.
This project implemented the blockchain as a method of sharing data quickly and securely between parts manufacturers, suppliers, and those assembling the cars. Their blockchain provides a secure means for each supplier to share their data all the while tracking changes in real-time and ensuring end-product compliance.
RELATED: HOW THE BLOCKCHAIN IS REVOLUTIONIZING THE ONLINE BANKING INDUSTRY
I had the pleasure of discussing XCEED and Groupe Renault’s use of blockchain technology with the project’s Vice President, Odile Panciatici. She noted that the benefits of blockchain become clear when you examine how it can change the workflows of her industry on a larger scale.
In reference to developing XCEED, the first collaborative blockchain project implemented by Groupe Renault, she notes that she, “quickly saw that for the customer, transparency and the responsibility of the company – and trust – in the industrial ecosystem would be a key asset for our industry.”
This emphasis on customer-focused transparency and trust is one of the benefits of using blockchain. Not only is it a highly effective data management tool, but it’s also highly secure and efficient. This ensures that each supplier’s data is handled securely, and when it comes time for compliance and regulatory checks, everything is where it should be.
Discussing the project in greater detail, Panciatici said it was built to, “focus on the compliance and the conformity of the car. Each car is made up of thousands of parts and when you design a car, you allocate each characteristic for each part.” This means that the overall regulatory compliance of each car is ensured “by many of characteristics to each part. If [regulators] ask for a demonstration of frontal crash regulation, the crash passes through a lot of components of the car. It’s in this way that you have many characteristics to be examined –and it takes time, especially since each part has its own supplier.”
Thus, it becomes clear when you examine all of the complexities of automotive manufacturing that many of the problems are rooted in data management, and many of these can be solved efficiently by using a blockchain-based system. Renault’s vision of the tech is transformative to the entire industry.
Panciatici underscored that while the “project was initiated by Groupe Renault, the purpose of the project is to be shared. If one OEM implemented the Blockchain on our own, it wouldn’t be very efficient. Blockchain’s technology demands to be shared, even with other industries.”
This touches on the collaborative note of the underlying technology, as well as the collaborative underpinnings of the automotive industry as a whole. The modern automotive industry is more interconnected than ever. But with this interconnectivity is the risk that one supplier’s or OEM’s innovations might be stolen or misused. Again, blockchain securely mitigates this issue.
When you examine blockchain from a higher level, you start to see how a secure and real-time data collection chain can be useful in a larger variety of use-cases. For example, self-driving technology has long been understood as a data problem. The more data that is collected through autonomous driving, the better the predictive algorithms can become, and thus the better the autonomous technology becomes.
However, all of this data also has the potential to be a security issue. Autonomous driving data will eventually consist of the collection of millions of people’s locations, travels, daily schedules, and more. Few would be okay with the collection of that much data – although our smartphones already capture most of this. But blockchain could be used as a solution here as well. Collecting and storing this data using blockchain technology would not only ensure encryption, but also that the data is only used for its intended purpose, building better autonomous tech.
Similarly, in the realm of ride-sharing, we can also see the benefits of using blockchain. One of the goals of blockchain technology is to remove the “middle-man” in communication and improve security. In ridesharing, there’s a lot of data that has to be passed between the rider, the driver, and the managing company. Blockchain is already being used as an efficient way to securely manage all this intermediary data, ensuring that each party handled responsibly.
But with all of these potential applications and benefits, what will likely be the most transformative to the automotive industry? That is likely to be decentralized data management for OEMs and part suppliers; and it’s become clear that Groupe Renault, in partnership with other industry leaders, intends to lead the way in this space.
