Cultural challenges impede organizations from becoming responsive, agile, or autonomic. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DOAs) can help address such issues.
The persistent Covit-18 pandemic is challenging all our
norms. We are starting to see huge financial losses in many sectors. But most
importantly, we are witnessing mega-shifts that will have profound impacts,
once the dust settles. A recent article
from McKinsey clearly articulates the post-Covid-19 cultural revolution
impacting organization of all sizes:
Many
leaders are reflecting on how small, nimble teams built in a hurry to deal with
the COVID-19 emergency made important decisions faster and better. What
companies have learned cannot be unlearned—namely, that a flatter organization
that delegates decision making down to a dynamic network of teams is more
effective.
As we discussed in an
earlier article – May 2020 (has it been that long?) – the Covid-19 lockdowns and shutdowns of businesses and government will
change us – are changing us. In this article, we are revising and expanding upon an essential trend powering autonomic enterprise:
Decentralized Automation Organizations.
The
Covid-19 pandemic is a Black Swan event par excellence. Many
industries such as manufacturers, pharmaceutical companies, and restaurants re-defining and re-organizing
themselves for Covid-19 products and services. Innovative startups are re-aligning
their services to accommodate constantly changing Covid-19 constraints.
Becoming an autonomic enterprise in motion is not an option
Recently,
Cisco’s former CEO, John Chambers, indicated that 50% of Fortune 500 companies would not
exist in 10 years. The importance
of Culture got accentuated in the post-Covid-19 era. Transformation
starts with Culture. The conventional “Org Chart” did not inspire
agility, change, or empowerment in the pre-Covid-19 age. Post-Covid-19, it
has been challenged and stressed to the limit. It is a model that is no longer
working – especially with the newer, technologically savvy, independent-minded,
and entrepreneurial younger generations.
The Covid-19 organizational
trends encompass smaller & flatter org charts, virtualization, and
innovative teams – all with an added emphasis on integrity and empowerment.
Flat Organizations
Organizations are becoming flatter – often not by choice.
More than ever, the lockdown, interruption of supply chains, and the emergence
of virtual work shifts are accentuating the need for innovation,
entrepreneurship, and autonomy, especially through challenging the archaic
hierarchical organization structures towards more decentralization and
innovation empowerment at the “edges.”
The top-down hierarchical organization structures are tired
and passé. They do not inspire innovation or digital transformation. Employee
empowerment has been elusive and hard to achieve within a rigidly hierarchical
organization.
Flattening organizations with increased communication, collaboration, and empowerment is an irreversible trend
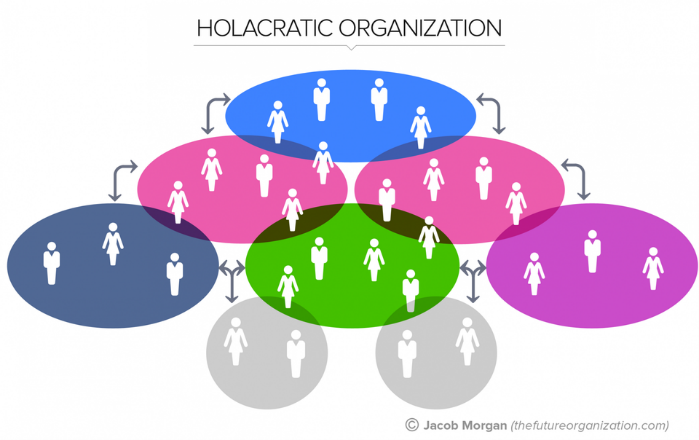
Jacob Morgan contrasts several emerging organizational models in the Future of Work. Emerging models include flat and holacratic organizations (vs. bureaucracies and hierarchies – and we know how well those functions!). Challenging traditional management around circles for specific projects and objectives is both liberating and transformational. The Covid-19 pandemic provides a wonderful opportunity for organizations to re-assess their rigid structures and flatten their organizations.
Virtuality
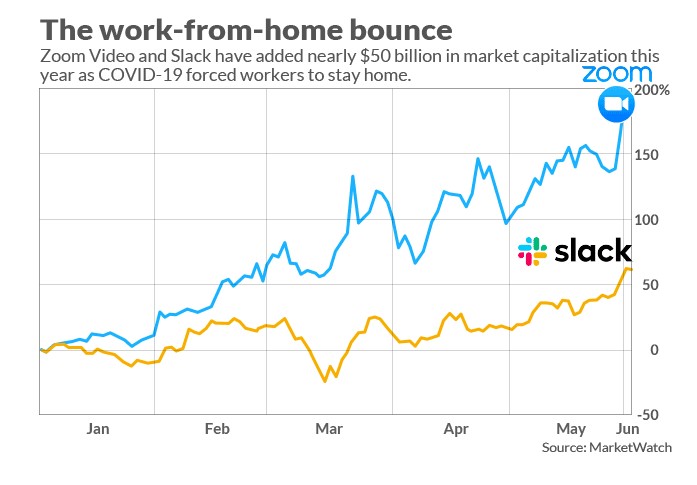
Virtuality
is another irreversible trend that has gained incredible traction in the
Covid-19 era. Collaboration and
virtualization tools such as Zoom and Slack – often essential for work-from-home-
have had an incredible run: 72%
of consumers had their first-ever virtual care visit during Covid-19. The
virtuality shift is complex and multi-faceted. The nine-to-five in the office
“normal” is being reset: Employees want greater
flexibility in the percentage of time they spent at home vs. office – the
breakdown is 51% office and 49% home.
Virtuality also has an inter-organizational dimension. The
notion of “virtual enterprises” or their predecessor “virtual
corporation” has been around for a while. The core idea is the ability for
organizations to deliver customized products and services quickly and globally.
This was an amazing vision coming from the
early 1990s. Another term that is used synonymously or embedded in the connotation of
a virtual enterprise is the “extended enterprise.” Basically, “a loosely
coupled, self-organizing network of firms that combine their economic output to
provide products and services offerings to the market.”
The extension beyond
the organizational boundaries involving inter-enterprise collaboration is
becoming critical in the Covid-19 era. The extended enterprise needs to
function as a coordinated whole – preferably seamless to the consumer or
customer. The core premise is creating very flexible and dynamic organizations that
can rapidly satisfy customers’ or consumers’ demands and needs.
As Mike Welsh points out: For a virtual organization to function, geographically
dispersed teams need the ability to communicate effectively. But that’s only
half the story. Decision-making has to be delegated and decentralized as well —
and that means using data to shake up your culture.
How could organizations achieve intra-
and inter-enterprise decentralization?
Enter Blockchain and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations.
Blockchain
As of the writing of this article, Bitcoin (BTC) has hit $17,000.
It is incredible to realize that this successful cryptocurrency’s governance is
decentralized. Blockchain
is the underlying technology for Bitcoin and most other cryptocurrencies. But
Blockchain is much more than that. Through intra-enterprise transactional
collaboration, Blockchain could empower geographically distributed networks of
teams.
As we discussed in Blockchain
for Master Data Management, Blockchain can also be a good backbone for many extended enterprise
applications. For instance, the Covid-19 pandemic highlighted the
vulnerabilities in supply chains. Blockchain is one of the critical
technologies that could address Supply Chain problems.
The digitally
extended enterprise can use all parts, products, suppliers, warehouses,
inventory, documentation, tracing, and financial transaction masters stored on
the Blockchain to function as an efficient and optimized pipeline. Through
Blockchain, organizations can enact governance, share data, and make autonomous
decisions on the Blockchain.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
What are DOAs? Here is a good
definition: “A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is an
organization where the rules of operation and organizational logic are encoded
as a smart contract on a blockchain … DAO’s […] formulation combines blockchain
technology, organizational structures, legal entities, workflow execution,
governance/voting, incentive structures, and contribution/work.”
Decentralization is at the core of the crypto-currency revolution,
and its importance is increasing in the post-Covid-19 era. The Bitcoin Foundation’s Manifesto states:
“the technology is completely decentralized, and the founder does not head
up an organization that sets the strategy, governance, and standards.” In
fact, Bitcoin was the first Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). There
is no centralized hub or authority that owns and runs “the Bitcoin.”
The governance is by consensus through Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs).
Contrast this how various solutions are governed in, say, centralized financial
organizations such as large Banks, with often archaic and rigid hierarchical structures.
Now, there are many DOAs and a robust DAO ecosystem.
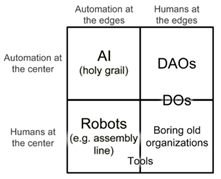
If you have been following Blockchain and cryptocurrencies –
especially Ethereum – you would have been exposed to Decentralized Autonomous
Organizations (DAOs). The governance, bylaws, and operation of a DAO use Smart
Contracts executing on the Blockchain. In other words, code running an
organization in a decentralized and distributed network. This approach has
several advantages. It allows all the shareholders and employees or other
stakeholders to agree and vote on decisions quickly. Since actual code is
executed for running the organization, it leaves little to the imagination to
interpret the governing policies. Furthermore, no central government or
authority is regulating a DAO. As we shall see, this is also a weakness of a
fully autonomous organization executing on the Blockchain.
“DAO” was introduced by Vitalik Buterin – the
inventor of Ethereum. As he describes it in a decentralized
organization guide: “it is an entity that lives on the internet and
exists autonomously, but also heavily relies on hiring individuals to perform
certain tasks that the automaton itself cannot do.” In his taxonomy of
automation, including automated agents through AI, Buterin characterizes a DAO
as ‘autonomous at the center’ but ‘humans at the edges.’ Thus, the operation,
governance of the organization are done through smart contracts executing on
the Blockchain. But humans are also participants and can be involved in A DAO
is a Blockchain application.
There are many
advantages and desirable features of DAOs. But there are also severe vulnerabilities
and disadvantages.
Blockchain is about
decentralization. Therefore, it is not surprising that Blockchain communities
and cooperatives seek and pursue non-traditional models for cooperation.
- Binance is one of the largest cryptocurrency
exchanges. According to Cointelegraph, “the business has been operating as an international,
decentralized team for over three years already. Remote working is an essential
part of the Binance culture.” - Open
Source in software has always fostered and promoted democratic collaboration.
These cultural trends are also giving rise to several community initiatives.
Open Source communities are organizations that encourage communication and
cooperation – which are, in essence, democratic and “flat.” - The
Ethereum Foundation
encourages collaboration for “development and education to bring
decentralized protocols and tools to the world that empower developers to
produce next-generation decentralized applications (dApps), and together build
a more globally accessible, more free and more trustworthy Internet.” - Another exciting initiative under the Linux Foundation – that promotes
Open Source projects, among them the umbrella Hyperledger collaboration for
Blockchain projects.
DAOs go beyond mere consortia and collaborations and create
governance and sharing capabilities on the Blockchain via dApps and Smart Contracts.
DAO Ecosystem
There are many categories of products and services that
support Decentralized Autonomous Organizations. The following illustrates the DAO
Ecosystem.

The George
Samman and David
Freuden report on
DAO: “A Decentralized Governance Layer for the Internet of
Value,” provides a good
overview of the various categories, tensions, and tradeoffs of DAOs.
The following provides the descriptions for the DAO
Ecosystems categories:
- Non-Tech Grants: Giving out grants for
social, economic, political, and community-based activities. - Investment DAOs (for-profit): DAOs that
invest capital into projects. - Decentralized Governance: These companies
are specifically working on building out tools and infrastructure to enable
decentralized governance capabilities to be built into DAOs. - DeFi DAOs (for-profit): These DAOs are
building out different parts of the Decentralized Finance stack, aka “money
legos.” - Protocols / Organizations: These are the
underlying protocols DAOs are being built on top of. Organizations/Companies
are also creating DAOs for token holders. - DSaaS (DAO Software as a Service):
Software platforms that provide infrastructure to build out DAOs.
Here are some organizations from some of the DAO Ecosystem
categories:
- DAOX:
In the Non-Tech Grants Category: “Crowdfunding campaigns are launched
using the Daox Protocol. Each DAO holds the raised funds and is managed by the
transparent voting of its token holders.” - Kava: In the
DeFi category:
“Kava is a multi-asset DeFi platform that offers stablecoins, loans, and
other financial services for users of major cryptocurrency assets including
BTC, XRP, BNB, and ATOM to name a few.” - Dash DAO:
In the Protocols/Organizations category: “In the Dash DAO, decisions are
made by the masternode network, a decentralized and permissionless network that
anyone in the world can be a part of.” - Pocket:
In the DSaaS category: “Pocket Network’s mission is to ensure the
sustainable decentralization of blockchain infrastructure…the most complete
system for blockchain APIs, by way of its all-inclusive relay network and
crypto-economic protocol.”
DOA in Post-Covid-19 Era
Two major cultural themes impact the emergence of DOAs in
this post-Covid-19 era: empowerment of the workers from the virtualized
work-from-home experiences and the need to optimize cross-enterprise
collaboration in the context of virtual or extended enterprises. DAOs address
both these significant trends.
It is becoming clear the challenges organizations face to become
responsive, agile, or – as our title suggests – autonomic are cultural. As the ecosystem illustrates,
slowly but surely, DOAs are becoming a reality.
Therefore, the advantages of DAOs can be summarized as
follows:
- DAOs
Empowering the Modern Digital Worker: there are irreversible trends in
workers or employees wanting to be more autonomous to become creative,
productive, and enjoy their work. We saw that this not a new trend. It is one
of the main characteristics of the cognitive knowledge worker. There are
several DAOs, and others will emerge. However, government liabilities and
recognition are still a considerable challenge – and will be for the
foreseeable future. Blockchain’s most likely scenario for cultural change will
be sub-organizations that leverage elements of a DAO approach. Smart Contracts
for organizational, worker, shareholder, or even customer empowerment can
accelerate and improve decision-making: the crowd’s wisdom
- DAOs
Enabling Inter-Organizational Collaborations: There are mostly yet to be
discovered opportunities for Blockchain assisting flat organizations. Supply
Chain is one of the killer applications leveraging Blockchain. The extended
enterprise involved in source-to-target of the supply chain needs to function
as a coordinated whole. DAOs support the governance, visibility, and
information as well as transaction sharing across the value chain. The core
premise is creating very flexible and dynamic organizations that can rapidly
satisfy customers’ or consumers’ demands and needs. DOAs can achieve this. Blockchain
is essential for digital transformation. There is no other technology on the
horizon that is decentralized, fault-tolerant, secure, and reliable for inter-enterprise
master-data and information sharing.
